BANK MARKETING
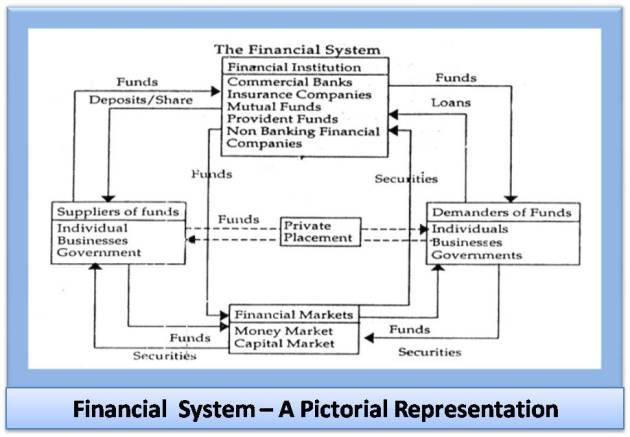
THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
The financial system consists of variety of institutions, markets and instruments that are related in the manner as represented diagrammatically below. It provides the principal means by which savings are transformed into investment. Given its role in the allocation of resources, the efficient functioning of the financial system is of critical importance to a modern economy. Finance manager negotiate loans from financial institutions, raise resources in financial marked and invests surplus funds in financial market. In very significant manner the Finance Manager manages the interface between the form and its financial environment, in tight rope walk situation..
Financial System plays a very important role in the development of a country. Through Financial System, entire money or money equivalents are channelized in such a way so that each sector of economy like industry, agriculture and services can be developed rationally. Financial sector can be dubbed as a locomotive force, as it makes you reach your own destination smoothly from the place or situation you happen to be facing. Thus, its contribution to economic development, can never be downplayed irrespective of geography and country.
ORIGIN OF THE WORD ‘BANK’
According to some economists the word ‘Bank’ has been derived from the German word BANC which means a Joint Stock Firm while others say that it has been derived from the Italian world ‘BANCO’ which means a heap or mound.
There is still another group of people who believe that word bank has been derived from the Greek work ‘BANQUE’ which means a bench. In the olden days, Jews entered into money transactions sitting on benches in a marked place. When a banker was not in a position to meet his obligations, the on which he was carrying on the money business was broken into pieces and was taken as bankrupt. Thus both the words Bank or bankrupt are said to have origin from the word ‘Banquet’.
DEFINITION OF BANK
According to Oxford English Dictionary, Bank is, “An establishment for custody of money received from or on behalf of, its customers. Its essential duty is the payment of the orders given on it by the customers, its profit mainly from the investment of money left unused by them”.
Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (Sec. 5(c)), has defined the banking company as, “Banking Company means any company which transacts business of banking in India”. According to Section 5B, “banking means the accepting of deposit of money from the public for the purpose of leading or investment, which are repayable on demand or otherwise and are withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise.”
Different economists, banking professionals and authorities explained their viewpoint regarding bank or commercial bank. It has been rightly said by A.K. Basu that a general definition of a bank or banking is by no means easy, as the concepts of banking differ from age to age, and country to country.
FINANCE AND BANKING IN INDIA
India is a vast country, before 1947, undivided India was equal to Europe excluding Russia in its area. It is situated in south of Asia. In spite of a part of Asia, it is separated from it. It is separated by Himalayas in North India. India has vast oceans in South, East and West. Due to its vastness it is also called sub continent. That vast country has given different names in different times. In Vedic period, it was called ‘Arya-V-arat’. In Bir period and ancient period, it as called Bharatvarash’. Perhaps due to fame of king Bharat, it was called ‘Bharatvarsh. Greek called it Indus on the name of river Sindh. Iranians called it Hindu. Chinese travelers called it Tienchu and Yintu. Ipsing called ‘Arya Desh’ and Brahmrashtra. Bible has called it Hoddu. In medieval period, it was called ‘Hindustan’ and Hind. European called it India. After Independence, it is return as Bharat Ganrajya or Indian Republic in Indian Constitution.
EVOLUTION OF THE MARKETING CONCEPT
The Role of marketing in the banking industry continues to change. For many years the primary focus of bank marketing was public relations. Then the focus shifted to advertising and sales promotion. That was followed by focus on the development of a sales culture.
Although all the elements of the marketing concept – customer satisfaction, profit integrated framework and social responsibility – will remain important, customer satisfaction must receive the greatest emphasis in the years ahead.
The chief concerns of most bank executives still focus on legal and regulatory issues, according to most surveys. Community banks are particularly concerned with eliminating barriers that give unfair advantages to financial services competitors, such as credit unions. However, another concern pertains to technology: keeping non bank competitors out of the payment system.
Bankers Identify Near-Team and Long Term Concerns
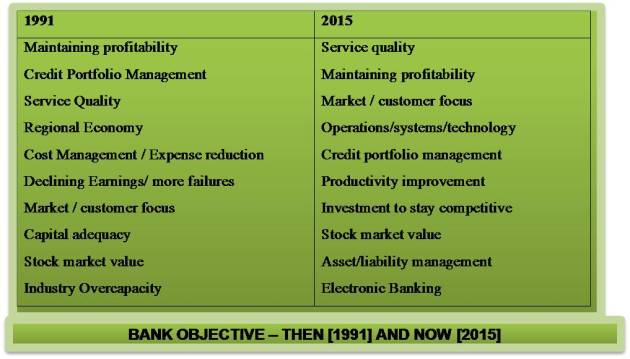
When this gateway system was first proposed, access to the Internet was very new and few banks had the resources and knowledge to set up their own direct-access lines for customers. Customers have shown a growing interest in online banking services, and banks have responded by quickly putting in place proprietary sites on the World Wide Web and offering PC banking.
Within the next five years, 93 percent of community bank executives surveyed say they plan to offer telephone banking, and 79 percent plan to offer PC banking.
When asked which technology holds the most potential for the future, bank executives identified call centers first. As customers continue the transition the transition into a high-tech world in which they want information and answers more quickly and accurately than ever before, call centers offer the ideal bridge. With 24-hour access to either automated information or live operators, customers do everything from check their accounts to apply for a loan. Bank executives also identified PC banking as having the most promise for the future, followed by Interest access and broad function kiosks.
MARKETING AND COMPETITION
In view of the declining profitability and productivity of the banking sector and extremely low rate of profit percentage, the determination of the financial health of the system requires drastic remedial measures not only to build up investor confidence but also to combat competition from all over. It is time that the pros and cons of the oncoming banking era are properly understood and advantage taken of various opportunities. This will require an efficient marketing approach to bank management in which target markets will be tackled successfully along with effective satisfaction levels and in which the usual basic elements – product, pricing, promotion and distribution will be taken care of in a proper format of an efficiently working marketing organization.
The nationalized banks must face competition from private banks, non-banking financial institutions, foreign banks and others. The competition is in the fields of deposits and credits, foreign trade, consumer credit and miscellaneous banking activities. The competition will benefit customers and force the banking system to raise its productivity, minimize expenses, and remain sensitive to evolving issues. Narasimham Committee Reports while recommending internal autonomy long with compliance with prudential norms suggested rule-based credit policies, fiscal balance and a gradual movement towards liberalization.
To deal with the competition from foreign banks, the Indian banks should go in for diversification and extension of services as well as expansion of products and business. Economic freedom and innovative spirit have contributed greatly to the success of the market-oriented financial sector in the Western countries. Directed credit and investment has done just the opposite. Interventionism is not necessarily bad provided it is associated with a committed leadership. Indian financial sector had for more than four decades, neither full economic freedom nor a well disciplined interventionism so that it cost operational flexibility as well as functional autonomy both of which were concerned with profitability performance and related factors.
MARKETING CONCEPTS
Its application to Banking, When we apply marketing to the banking industry, the bank marketing strategy can be said to include the following –
i) A very clear definition of target customers.
ii) The development of a marketing mix to satisfy customers at a profit for the bank.
iii) Planning for each of the ‘source’ markets & each of the ‘use’ markets (A Bank needs to be doubly market – oriented – it has to attract funds as well as were of funds & services.
iv) Organization & Administration.
BANK MARKETING
We define bank marketing as follows: “Bank marketing is the aggregate of functions, directed at providing services to satisfy customers’ financial (and other related) needs and wants, more effectively and efficiently that the competitors keeping in view the organizational objectives of the bank”. Bank marketing activity. This aggregate of functions is the sum total of all individual activities consisting of an integrated effort to discover, create, arouse and satisfy customer needs. This means, without exception, that each individual working in the bank is a marketing person who contributes to the total satisfaction to customers and the bank should ultimately develop customer orientation among all the personnel of the bank. Different banks offer different benefits by offering various schemes which can take care of the wants of the customers.
Marketing helps in achieving the organizational objectives of the bank. Indian banks have duel organizational objective – commercial objective to make profit and social objective which is a developmental role, particularly in the rural area.
Marketing concept is essentially about the following few thing which contribute towards banks’ success:
1) The bank cannot exist without the customers.
2) The purpose of the bank is to create, win, and keep a customer.
3) The customer is and should be the central focus of everything the banks does.
4) It is also a way of organizing the bank. The starting point for organizational design should be the customer and the bank should ensure that the services are performed and delivered in the most effective way. Service facilities also should be designed for customers’ convenience.
5) Ultimate aim of a bank is to deliver total satisfaction to the customer.
6) Customer satisfaction is affected by the performance of all the personal of the bank.
All the techniques and strategies of marketing are used so that ultimately they induce the people to do business with a particular bank. Marketing is an organizational philosophy. This philosophy demands the satisfaction of customers needs as the pre-requisite for the existence and survival of the bank. The first and most important step in applying the marketing concept is to have a whole hearted commitment to customer orientation by all the employees. Marketing is an attitude of mind. This means that the central focus of all the activities of a bank is customer. Marketing is not a separate function for banks. The marketing function in Indian Bank is required to be integrated with operation.
Marketing is much more than just advertising and promotion; it is a basic part of total business operation. What is required for the bank is the market orientation and customer consciousness among all the personal of the bank. For developing marketing philosophy and marketing culture, a bank may require a marketing coordinator or integrator at the head office reporting directly to the Chief Executive for effective coordination of different functions, such as marketed research, training, public relations, advertising, and business development, to ensure customer satisfaction. The Executive Director is the most suitable person to do this coordination work effectively in the Indian public sector banks, though ultimately the Chief Executive is responsible for the total marketing function. Hence, the total marketing function involves the following:
a) Market research i.e. identification of customer’s financial needs and wants and forecasting and researching future financial market needs and competitors’ activities.
b) Product Development i.e. appropriate products to meet consumers’ financial needs.
c) Pricing of the service i.e., promotional activities and distribution system in accordance with the guidelines and rules of the Reserve Bank of India and at the same time looking for opportunities to satisfy the customers better.
d) Developing market i.e., marketing culture – among all the customer-consciousness ‘Personnel’ of the bank through training.
Thus, it is important to recognize the fundamentally different functions that bank marketing has to perform. Since the banks have to attract deposits and attract users of funds and other services, marketing problems are more complex in banks than in other commercial concerns.
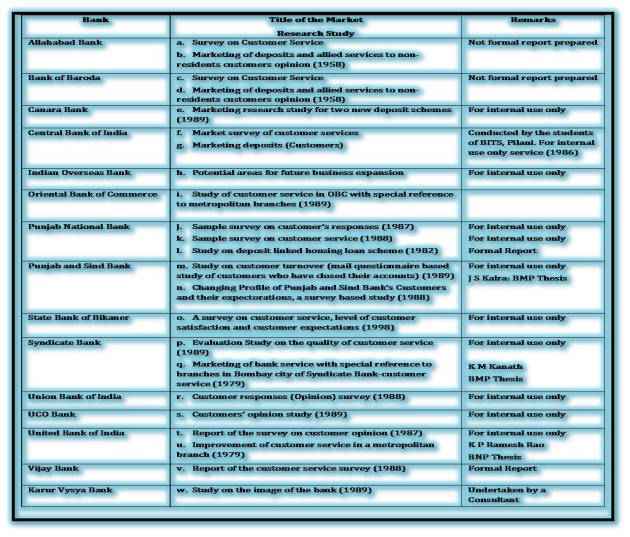
MARKET RESEARCH IN INDIAN BANKS
After enquiring with all the public and 14 private sector banks whether they had undertaken any market research studies. The following board areas of market research were considered for the study:
(a) New service development,
(b) New service product acceptance,
(c) Research and development of existing financial service,
(d) Bank images study,
(e) Measuring bank’s advertising effectiveness,
(f) Measurement of market potentials,
(g) Market research of competitive service products,
(h) Customer’s opinion study,
(i) Customer profile study, and
(j) Market share analysis.
In response to the inquiry information was received from 17 banks. Out of these banks, 14 are public sector banks and 3 are private sector banks. Two nationalized banks and two private sector banks informed that they have not conducted any markets research studies.
Information regarding Bankwise Market Research Studies
| Bank | Title of the Market Research Study | Remarks |
- Allahabad Bank
- Bank of Baroda
- Survey on Customer Service
| - Marketing of deposits and allied services to non-residents customers opinion (1958)
| Not formal report prepared.MP Ranade: BMP Thesis. |
- Canara Bank
- Marketing research study for two new deposit schemes (1989)
|
| For internal use only |
- Central Bank of India
- Market survey of customer services
- Marketing deposits (Customers)
|
| Conducted by the students of BITS, Pilani. For internal use only service (1986) |
- Indian Overseas Bank
- Potential areas for future business expansion
|
| For internal use only |
- Oriental Bank of Commerce
- Study of customer service in OBC with special reference to metropolitan branches (1989)
|
| R Upendran MBP Thesis |
- Punjab National Bank
- Sample survey on customer’s responses (1987)
- Sample survey on customer service (1988)
- Study on deposit linked housing loan scheme (1982)
|
| For internal use onlyFor internal use only Formal Report |
- Punjab and Sind Bank
- Study on customer turnover (mail questionnaire based study of customers who have closed their accounts) (1989)
- Changing Profile of Punjab and Sind Bank’s Customers and their expectorations, a survey based study (1988)
|
| For internal use onlyJ S Kalra: BMP Thesis |
- State Bank of Bikaner
- A survey on customer service, level of customer satisfaction and customer expectations (1998)
|
| For internal use only |
| 10. Syndicate Bank | - Evaluation Study on the quality of customer service (1989)
- Marketing of bank service with special reference to branches in Bombay city of Syndicate Bank-customer service (1979)
| For internal use onlyK M Kanath BMP Thesis |
| 11. Union Bank of India | - Customer responses (Opinion) survey (1988)
| For internal use only |
| 12. UCO Bank | - Customers’ opinion study (1989)
| For internal use only |
| 13. United Bank of India | - Report of the survey on customer opinion (1987)
- Improvement of customer service in a metropolitan branch (1979)
| For internal use onlyK P Ramesh Rao BNP Thesis |
| 14. Vijay Bank | - Report of the customer service survey (1988)
| Formal Report |
| 15. Karur Vysya Bank | - Study on the image of the bank (1989)
| Undertaken by a Consultant |
Most of these market research studies were conducted for internal use and no formal reports were prepared. It is important to note the subject or issue researched by the bank. The most important subject for market research in terms of the number of studies conducted, is the customer service / customer’ profile opinion studies. Few banks have conducted even more than one customer service / opinion studies.
INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING IN BANKING INDUSTRY
The various other factors which have led to the increasing importance of marketing in the banking industry are categorized as follows:
POLITICAL & ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
The Indian economy embarked on the process of economic reform and various policy measures initiated by the government resulted in the increasing competition in the banking industry, thereby highlighting the importance of effective marketing. The Narasimhan Committee Report evidence of the Government’s desire to ‘re-regulate’ the banking industry so as to encourage efficiency through competition. The Government initiatives include:
DEREGULATION OF INTEREST RATES
The bank may reduce their Minimum Lending Rates so as to attract customers (individual and corporate). Such reduction in lending rates reduce the spread between the deposit rates and lending rates, i.e. the banks margins would decline and they would have to increase their volumes or provide attractive services so as to maintain profits. This calls for bank marketing.
INCREASING EMPHASIS ON BANK PROFITABILITY
With the Narasimhan Committee Report, banks have been directed to improve their efficiency, productivity and profitability. Banks are required to be self-sufficient. In fact, the report has adopted the BIS standards of capital adequacy (though in a phased manner).
FOREIGN BANKS
Foreign banks offer stiff competition to the Indian Banks and with their superior services and technologies offer them a competitive advantage. Thus Indian Banks have to effectively apply marketing concepts to attract customers.
ENTRY OF NEW PRIVATE BANKS
In the early ‘90s new competition emerged in the form of new Private Banks, who brought along with them a high technology-based banking matching with International Standards and have made a significant dent in the banking business by capturing substantial share in the profits of the banking industry.
REDUCTION OF STATUTORY LIQUIDITY RATIO
With the Government’s aim of reducing the SLR to 25 percent, the banks will have surplus funds for which they will have to attract users.
SOCIAL ENVIRONMENT
INCREASING URBANIZATION, EDUCATION AND AWARENESS: The higher literacy level, migration to urban areas and higher awareness due to the boom in the mass media have important implications for the retail banker. He needs to be conscious of the fact the increasing proportion of people are aware of financial service and are, therefore demanding and expecting higher quality services.
INCREASING URBANIZATION, EDUCATION AND AWARENESS: The higher literacy level, migration to urban areas and higher awareness due to the boom in the mass media have important implications for the retail banker. He needs to be conscious of the fact the increasing proportion of people are aware of financial service and are, therefore demanding and expecting higher quality services.
Decline in Traditional Indian Values (Borrowing as Taboo), Rising Consumerism, Rise in the Percentage of Working Women.
TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT
Modernization of Technology has facilitated the introduction of new banking services as to attract new customers. An example of this is the ‘Automated Teller Machines’ or the facility of ‘Any Time Money’. Also in foreign countries, banks are experimenting with money transmission at Point of sale, e.g., petrol station linked with banking network.
CREDIT IS EASIER TO OBTAIN
GROWING IMPORTANCE OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS: Fixed Deposits being offered by the NBFC’s are very attractive for the public, because of the wide gap of interest rates offered by banks on term deposits and that offered by the NBCS’s. further, they offer a variety of specialized services to their customers so as to attract and retain them.
Disintermediation: The increasing role of capital markets in mobilizing funds is reducing the importance of banks as intermediaries. Companies are directly approaching the savers through the capital markets. Mutual funds help in attracting the small investors who do not want to take much risk.
MARKETING CONCEPTS – ITS APPLICATION TO BANKING
When we apply marketing to the banking industry, the bank marketing strategy can be said to include the following:
- A very clear definition of target customers.
- The Development of marketing mix to satisfy customers at a profit for the bank.
- Planning for each of the ‘source’ markets and each of the ‘user’ markets (A bank needs to be doubly market – oriented – its has to attract funds as well as users of funds and services).
- Organization and Administration.
CONSUMER BEHAVIOR AND SEGMENTATION
Need for segmentation
Philip Kotler has described the dilemma of the seller (especially, a seller dealing with masses, e.g. banks) as follows:
“How the seller determines which buyer’s characteristics produce the best partitioning of a particular market? The seller does not want to treat all customers alike nor does he want to treat them all differently”.
Banks deal with individuals, group of persons and corporates, all of whom have their likes and dislikes. No bank can afford to assess the needs of each and every individual buyer (actual or potential).
Segmentation of the market into more or less homogenous groups, in terms of their needs and expectations from the banking industry, provides a solution to this problem.
This involves dividing the market into major market segments, targeting one or more of this segments, and developing products and marketing programs tailor-made for these segments.
In the first segmentation, the market is divided from a unitary whole, to groups of buyers who might require separate products and marketing mix. The marketer typically tries to identify different segments in the market and develop profiles of resulting market segments.
The second step is market targeting in which each segment’s attractiveness is measured and a target segment is chosen based on tits attractiveness.
The third step is product positioning which is the act of establishing a viable competitive position of the firm and its offer in the target segment chosen.
In the process of segmentation, the market can be divided into major segments which are gross slices of the market, or into smaller specially formed segments, otherwise known as niches. Niche customers have a specific set of needs which the markerter tries to address. While a market segment attracts several competitors, a niche attracts fewer competitors and therefore, a company should clearly define its target segment and devise strategies to target the customer, so that it has a competitive advantage in the segment.
These concepts can be applied in personal banking by an Indian Bank. Traditionally, Indian Banks have not had any conscious strategy for selecting customers from the personal banking area, apart from some banks which have a geographic concentration strategy such as concentrating on a particular region or state. These banks will have to segment the market on certain basis, and identify market segments or niches which they want to cater to. For example, a bank like SBI may not be able to cater high income groups (say, managers, professional, NRIs, etc. who earn above Rs. 4,00,000 p.a. and who want a higher quality of products / services and who are willing to pay for them), as the services required by such a profile of customers are entirely different from the kind of products / services SBI can offer.
Initiation of Segmentation in India
Station Bank of India was the first Indian Bank to adopt the concept of market segmentation. In 1972, it reorganized itself on the basis of major market segments dividing customers on the basis of activity and carved out 4 major market segments, viz. Commercial and Institutional, Small Industries and Small Business Segment, Agriculture, Personal and Services Banking. The objectives of this scheme were:
- Deeper penetration and coverage of market by looking outwards.
- Adequate flexibility of organization to accommodate growth and rapid change,
- Delegation of work for releasing senior management for more futuristic tasks.
Criteria for Segmentation
Segmentation in a right fashion makes the ways for profitable marketing. This helps policy planner in formulating and innovating the policies and at the same time also simplifies the task of bank professionals while formulating an innovating the strategic decisions. The following criteria make possible rig segmentation.
An important criterion for market segmentation the economic system in which we find agricultural sector, industrial sector, services sector, household sector, institutional sector and rural sector requiring of weightage while segmenting.
Agricultural Sector: In the agricultural sector, there are four category rise since the needs of all the categories cant’s be identical.
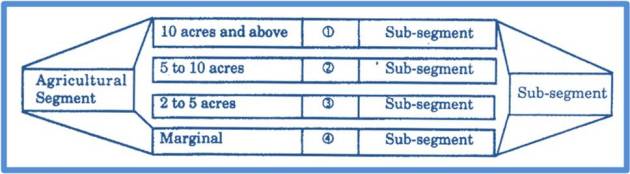
The mechanization of agriculture, the improved or scientific system of activation, the help of nature, the magnitude of risk, the availability infrastructural facilities influence the level of expectations vis-à-vis the needs and requirements. The banking organization are supposed to know and under stand the changing requirements of different categories of farmers.
Industrial Sector: The banking organizations subserve the interests of the industrial sector. The large-sized, small-sized co-operative and tiny industries use the services of banks. The expectations of all the categories cant’s be uniform.
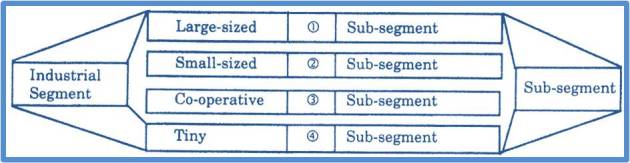
The banking organizations are supposed to have an indepth knowledge of the changing needs and requirements of the industrial segment.
Services sector: It is an important sector of the economy where the banking organizations get profitable business. The two categories of organizations such as profit-making and not-for-profit making are found important in the very context.

The banking organizations need to identify the changing needs and requirements of the services sector. With the frequent use of information technologist and with the mounting pressure of inflation and competition, we find a change in the hierarchy of needs.
Household Sector: This is also constitutes an important sector where different income group have different needs and requirements. in below figure we find the different segments of the household sector.
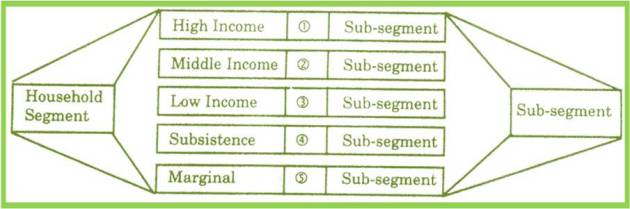
Household Segment: The high income group, middle income group, low income group, substance level group and marginal income group have different hierarchy of need which influence the level of their expectations.
Gender Segment: In the gender segments, we find male and female having different needs and requirements. The banking organizations are supposed to identify the level expectations of both sexes.
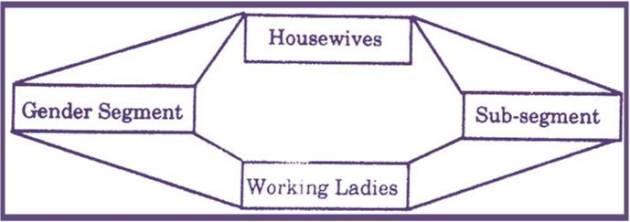
Some of the women are housewives and therefore they have different need and requirements whereas some of them are working ladies having different needs and requirements.
In the profession segments, we find different categories of professions an therefore we find a change in their needs and requirements.
The technocrats, bureaucrats, corporate executives, intellects, white and blue – collar employees have different needs and requirements and therefore the banking organizations should know their expectations.
Some of the organizations are known as cultural organizations, some of them are not for –profit making, some of them are philanthropic and some of them are related to trade and commerce. The emerging trends in the social transformation process determine the hierarchy of needs.
Markets segmentation thus simplifies the task of understanding the customers/prospects. The bank professional find it convenient to formulate and innovate the marketing mix of world class which simplify the process of excelling competition.
In the Indian perspective where we find agrarian economy contributing substantially to the transformation of national economy, it is pertinent that the banking organizations assign due weightage to the rural sector of the economy where we find tremendous opportunities.
The urbanization is likely to gain the momentum and villages, outskirts of big towns and cities are to be developed on a priority basis. Almost all the organizations are to get tremendous opportunities there. The marketing resources if of innovative nature would make the ways for capitalizing on the same profitably.
MARKETING MIX FOR BANKING SERVICES
The formulation of marketing mix for the banking services is the prime responsibility of the bank professional who based on their expertise and excellence attempt to market the services and schemes profitably.
The bank professionals having world class excellence make possible frequency in the innovation process which simplify their task of selling more but spending less. The four submixes of the marketing mix, such as the product mix, the promotion mix, the price mix and the place mix, no doubt, are found significant even to the banking organizations but in addition to the traditional combination of receipts, the marketing experts have also been talking about some more mixes for getting the best result. The “People” as a submix is now found getting a new place in the management of marketing mix. It is right to mention that the quality of people/employees serving an organization assumes a place of outstanding significance. This requires a strong emphasis on the development of personally-committed, value-based, efficient employees who contribute substantially to the process of making the efforts cost effective. In addition, we also find some of the marketing experts talking about a new mix, i.e. physical appearance. In the corporate world, the personal care dimension thus becomes important. The employees re supposed to be well dressed, smart and active. Besides, we also find emphasis on “Process” which gravitates our attention on the way of offering the services. It is only not sufficient that you promise quality services. It is much more impact generating that your promises reach to the ultimate users without any distortion. The banking organizations, of late, face a number of challenges and the organizations assigning an overriding priority to the formulation processes get a success. The formulation of marketing mix is just like the combination of ingredients, spices in the cooking process.
THE PRODUCT MIX: The banks primarily deal in services and therefore, the formulation of product mix is required to be in the face of changing business environmental conditions. Of course the public sector commercial banks have launched a number of polices and programmers for the development of backward regions and welfare of the weaker sections of the society but at the same it is also right to mention that their development-oriented welfare programmes are not optimal to the national socio-economic requirements. The changing psychology, the increasing expectations, the rising income, the changing lifestyles, the increasing domination of foreign banks and the changing needs and requirements of customers at large make it essential that they innovate their service mix and make them of world class. Against this background, we find it significant that the banking organizations minify, magnify combine and modify their service mix.
It is essential that ever product is measured up to the accepted technical standards. This is due to the fact that no consumer would buy a product which contains technical faults. Technical perfection in service is meant prompt delivery, quick disposal, presentation of right facts and figures, right filing proper documentation or so. If computers starts disobeying the command and the customers get wrong facts, the use of technology would be a minus point, and you don’t have any excuse for your faults.
PRODUCT PORTFOLIO: The bank professional while formulating the product mix need to assign due weightage to the product portfolio. By the concept product portfolio, emphasis is on including the different types of services/ schemes found at the different stages of the product life cycle. The portfolio denotes a combination or an assortment of different types of products generating more or less in proportion to their demand. The quality of product portfolio determines the magnitude of success. It is excellence of bank professionals that help them in having a sound product portfolio.
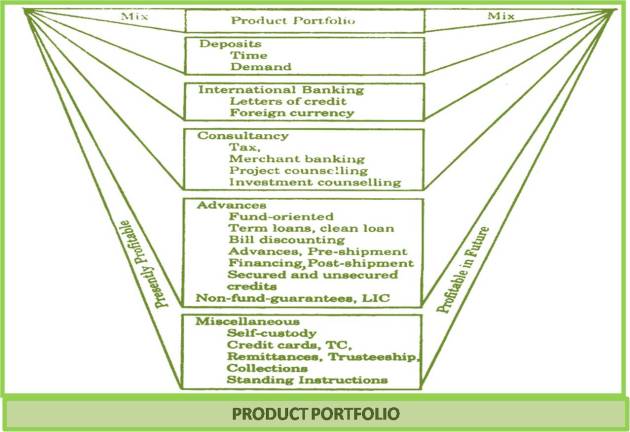
We find the composition of a family sound, if members of all the age groups are given due place. Like this, the composition or blending of a service mix is considered to be sound, if well established and likely to be profitable schemes are included in the mix. It is against this background that a study and analysis of product portfolio is found significant. The bank professionals are supposed to perform the responsibility of composing the same. A sound product portfolio is essential but its process of constitution is difficult. An organization with a sound product portfolio gets a conducive environment and successes in increasing the sensitivity of marketing decisions. The banking organizations need a sound product portfolio and the bank professionals bear the responsibility of getting it done suitably and effectively.
If the banks rely solely on their established services and schemes, the multidimensional problems would crop up in the long run because when the well established services/schemes would start saturating or generating losses, the commercial viability of banks would of course, be questioned. The banking organizations relying substantially on a profitable scheme and ding nothing for new scheme likely to get a profitable market in the future is to face is to face a crisis like situation. It is in this context, that we find designing of a sound product portfolio essential to an organsition. We can’t deny that the product portfolio of the foreign banks is found sound since they keep their eyes moving. The innovation, diffusion, adoption and elimination processes are taken due care. The public sector commercial banks need to innovate their service and this makes a strong advocacy in favour of analyzing the product portfolio.
DESIGNING AN ATTRACTIVE PACKAGE
In the formulation of product mix for the banking organization, the designing of package is found important. In this context, we find packaging decision related to the formulation of a mix of different schemes and services. Developing an attractive package required professional excellence and therefore, the bank professionals are required to be aware of the different key issues influencing the formulation process. What the package should basically be or do for the particular target. We re aware of the fact that a number of schemes and services are included in the service mix of bank product and all the services or schemes can’t be preferred by all. Of course we find some of the public sector commercial banks now evincing stage. This makes it essential that a bank manager thinks in favour of developing a package. The importance of packaging can’t be underestimated considering the functions it performs and the effects which we witness in the process of attracting and satisfying the customers. In addition to other aspects, it is also pertinent that a bank manager is familiar with the package developed by the leading competitive banks since this would help them in innovating the package. It is an important component of the product mix and a bank manager while formulating or designing a package needs to assign due weightage to the formulation process. While developing a package, it is essential that the packages offered are efficacious in establishing an edge over the packages of competitors. Thus needs and preferences of the target market in addition to the packages offered by the competitors need due weightage while designing a package.
In the designing process the bank professionals can make a package, an ideal combination of both, the core and peripheral services. The main thing in the process is to make it profitable, convenient and productive to the customers so that they prefer to transact with the bank. For the bank professional, it is an important persuasive efforts that helps in increasing the business even without developing or innovating the services or schemes.
PRODUCTR DEVELOPEMNT: In almost all the services, the development of a product is an ongoing process. The banking organizations also need to develop new services and schemes. We can’t deny that the development of product specially in the banking services is found diffcult since they don’t have any discretion, however they can do it, of course in a limited way. By minifying, combining, modifying and magnifying, the banking organizations can give to the services or scheme a new look. The regulations of the Reserve Bank of India, no doubt stand as a barrier but professionally sound marketers make it possible even without violating the rules and regulations. The banking organizations in general have been found developing product by including some new properties or features. Generally we find two process for the development of product. The first process is found proactive since the needs of the target market are anticipated and highlighted. The second process is reactive and in this context the banks respond to the expressed needs of the target.
PROACTIVE PROCESS: In the pro-active process, we find product to market needs. This makes it essential that the branch managers are aware of the changing needs of the target market. There are six stages for the development of the product, such as idea generation, screening of the concept, assessing of market potential, analyzing the cost, test marketing and final commercial launching. The bank professionals have to be careful at all the stages so that whatever the services or schemes are developed are found instrumental in getting a positive response. The customers and competitors help bank professional substantially in generating a new idea. The screening of the product concept focuses on the process of narrowing down the list of the ideas generated to a small number of concepts.
The assessment of market potential is the third stage in which we find scanning of the market potentials at the apex level. The branch managers can assess the potential sin their command areas.
The fourth stage draws our attention on analyzing the cost on the basis of a cost-benefit analysis and the fifth stage before launching is test marketing which is found instrumental in minimizing the risk element. And finally, we find commercial launching. The Reserve Bank of India is also required to make the regulations liberal so that the pubic sector commercial banks get an opportunity to make their services or schemes internationally competitive. The unfair practices, illegitimate steps should be checked but fair practice should essentially be promoted to make the business environment conductive.
PROMOTION MIX: In the formulation of marketing mix the bank professionals are also supposed to blend the promotion mix in which different components of promotion such as advertising, publicity, sales promotion, word-of-mouth promotion, personal selling and telemarketing are given due weightage. The different components of promotion help bank professionals in promotion the banking business.
Advertising: Like other organizations, the banking organizations also us this component of the promotion mix with the motto of informing, sensing and persuading the customers. While advertising, it is essential that we know about the key decision making areas so that its instrumentality helps bank organization both at micro and macro levels.
Finalizing the Budget: This is related to the formulation of a budget for advertisement. The bank professionals, senior executives and even the police planners are found involved in the process. The formulation of a sound budget is essential to remove the financial constraint in the process. The business of a bank determines the scale of advertisement budget.
Selecting a Suitable vehicle: There are a number of devices to advertise, such as broadcast media, telecast media and the print media. In the face of budgetary provisions, we need to select a suitable vehicle. The latest developments in the print technology have made print media effective. The messages, appeals can be presented in a very effective way.
Making Possible creativity: The advertising professionals bear the responsibility of making the appeals, slogans, messages more creative. The banking organizations should seek the cooperation of leading advertising professionals for that very purpose.
Instrumentality of branch managers: At micro level, a branch manager bears the responsibility of advertising locally in his / her command area so that the messages, appeals reach to the target customers of the command area. Of course we find a budget for advertisement at the apex level but the business of a particular branch is considerably influenced by the local advertisements. If we talk about the cause-related marketing, it is the instrumentality of a branch manager that makes possible the identification of local events, moments and make advertisements condition-oriented.
Public Relations: Almost all the organization need to develop and strengthen the public relations activities to promote their business. We find this component of the promotion mix effective even in the banking organizations. We can’t deny that in the banking services, the effectiveness of public relations is found of high magnitude. It is in this context that we find a bit difference in the designing of the mix of promoting the banking services. Of course in the consumer goods manufacturing industries, we find advertisements occupying a place of outstanding significance but when we talk about the service generating organizations in general and the banking organizations in particular, we find public relations and personal selling bearing high degree of importance. It is not meant that the banking organizations are not required to advertise but it is meant that the bank executives unlike the executives of other consumer goods manufacturing organizations focus on public relations and personal.
Personal Selling: The personal selling is found instrumental in promoting the banking business. It is just a process of communication in which an individual exercise his/her personal potentials, tact, skill and ability to influence the impulse buying of the customers. Since we get in immediate feed back, the personal selling activities energies the process of communication very effectively.
The personal selling in an art of persuasion. It is a highly distinctive form of promoting sale. In personal selling, we find inter-personal or two-way communication that makes the ways for a feed back. There is no doubt in it that the goods or services are found half sold when the outstanding properties are well told. This are of telling and selling is known as personal selling in which an individual based on his/her expertise attempts to transform the prospects into customers.
Dynamics of Personals Selling
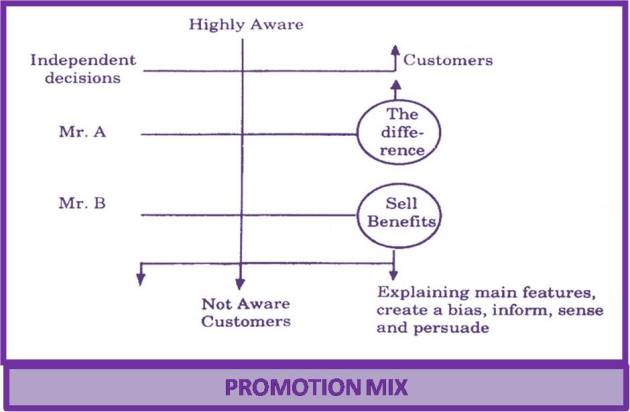
The dynamics of personal selling are found instrumental in activating the selling activities. Sales preparations are considered most crucial for the actual sales. Pre-sale activities and post-sale services can’t be left neglected to improve the marketing activities. The customers may be interested in knowing the main features of the services, how a particular service would help them, rationale behind the technical services and proof in regard to its uses. The pre-sale activities would bring the positive results, if preparations are adequate.
Some of the customers are found highly aware of the developments, they are found well informed. On the other hand, we also find other category of customers who are in dark. Here, the branch managers are expected to match the level of awareness of customers. As for instance, Mr. A goes up the matrix but Mr. B has not enough time for the branch managers. The branch managers are supposed to prepare a synopsis of their sales talk. Not surprisingly the highly aware customers are found in apposition to make independent decisions and know all about. While selling to the less aware customers, the managers should stress on the main features of the services and the expected benefits of these services.
Sales Promotion: It is natural that like other organisations, the banking organizations also think in favour of promotional incentives both to the bankers as well as the customers. The banking organizations make provisions for incentives to the bankers and call this bakers’ promotion. Like this, the incentives offered to the customers are known as customers’ promotion. There are a number of tools generally used in the different categories of organizations in the face of the nature of goods and services sold by them. The gift, contests, fairs and shows, discount and commission, entertainment and traveling plans for bankers, additional allowances, low interest financing and retalitary are to mention a few found instrumental in promoting the banking business.
As and when the banking organizations offer new services and schemes, the tools of sales promotion are required to be innovated. This is with the motto of stimulating the new and old customers. An important thing in the very context is the changing needs and requirements of customers/prospects. The bank professionals bean outstanding task of studying the competitors’ strategies which would he them in initiating the process of innovation. Here it is important to mention the promotional incentives to the customers would focus on decisions related to the selection of a tool. There are a number of considerations to streamline the process. The bank professionals are supposed to study the market conditions and make necessary suggestions, specially regarding the incentives.
It is a blending process and bank professional have to be sure the whatever the provisions, they make are fulfilled on priority basis. More incentives more efficiency or a vice-verse conditions more efficiency, more-incentives motivate bankers substantially.
Word-of-Mouth Promotion: Much communication about the banking services actually take place by word-of-mouth information which is also known as word-of-mouth promotion. In the banking industry, we find use of different components of promotion and in the context it is essential that we also talk about word-of-mouth communication which makes the process of influencing the prospects effective by sensitizing the word-of-mouth recommendations. The persons engaged in communication, the hidden salesforce who play an incremental role in increasing the demand. An important question regarding the word-of-mouth communication is related to its intensity of sensitizing the persuasion process.
The problem before the bank professionals is to identify the persons to be included in the list of word-of-mouth promoters. It is supposed that a bank manager is well aware of the social composition of his/her command area. The oral publicity plays an important role in eliminating the negative comments and improving the services. This helps you know the feed back which may simplify the task of improving the quality of services.
It is important that a branch manager has an in-depth knowledge of his/ her command area and a list of word-of-mouth promoters is prepared. Organizing dinner, offering to them a gift and seeking their cooperation are the process to use this tool of promotion. A satisfied group of customers is considered to be the most successful hidden promoters. A branch manager showing his/her excellence in improving the quality of services in his/ her command area, establishing an edge over the services of the competing banks, promoting LGD marketing (lunch, golf, dinner marketing) successds in instrumentalist the word-of-mouth promotion. It is against this background that this component of the promotion mix is found getting due place.
In this component of the promotion mix, we find two important considerations, first the bank professionals are required to make it sure that the promised services reach to the ultimate users and second, the word-of-mouth promoters are offered small but new incentives which have not been offered by their competitors. The list of word-of-mouth promoters is to be based on a survey result or on the personal experiences of a branch manager. A revision in the list is made possible as and when circumstances necessitate so. The innovative peripheral services offered by the banks are well publicized and the word-of-mouth promoters focus on the same intelligently.
THE PRICE MIX
In the formulation of product mix, the pricing decisions occupy a place of outstanding significance. The pricing decisions or the decisions related to interest and fee or commission charged by banks are found instrumental in motivating or influencing the target market. The Reserve Bank of India and the Indian Banking Association are concerned with the regulations. The rate of interest is regulated by the RBI and other charges are controlled by the Indian Banking Association. To be more specific in the Indian setting, we find this component of the marketing mix significant because the banking organizations are also supposed to subserve the interests of weaker sections and the backward regions. The public sector commercial banks in particular are supposed to play developmental role with societal approach. It is natural that this specific role of the public sector commercial banks complicate the problem of pricing.
Pricing policy of a bank is considered important for raising the number of customers vis-à-vis the accretion of deposits. Of course, there are a number of factors to influence the process but it is also right to mention that the key role in the entire process is played by the Reserve Bank of India. A National Consumer Survey Conducted by the L.H. Associates reveals that the quality of Consumer service was one of the three top issues and the consumers ranked the quality of their bank relationships as even more important than the fees charged for the services. To be more specific when we find a number of domestic and foreign banks working in the Indian economy, the Reserve Bank of India bears the responsibility of making the business environment conductive. The non-banking organizations and foreign banks have been found attracting customers by offering to them a number of incentives. The potential customers or investors frame their investment plans in the face of pricing decisions made by the banking organizations. While formulating the pricing strategies, the banks have also to take the value satisfaction variable into consideration. The value and satisfaction can’t be quantified in terms of money since it differs from person to person, keeping in view the level of satisfaction of a particular segment, the banks have to frame their pricing strategies. The policy makers are required to be sure that the service offered by them are providing satisfaction to the customers concerned. The pricing decisions may be to bit liberal, if the potential customers are found shifting to the non-banking investments. In this context, it is pertinent that pricing is used as motivational tool.
The banking organizations are required to frame two-fold strategies. First, the strategy is concerned with interest and fee charged and second, the strategy is related to the interest paid. Since both the strategies throw a vice-versa impact, it is pertinent that banks attempt to establish a correlation between the two. It is essential that both the buyers as well as the sellers have a feeling of winning as shown in figure.
The banks have to take the value satisfaction variable into consideration while designing the pricing strategies. McIver and Naylor opine that a marketing manager has to regard price as a variable to be traded off against product quality and promotion rather that as an absolute where the lowest price is not desirable.
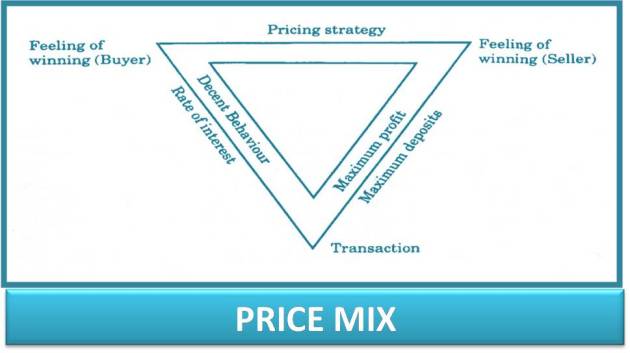
The RBI has to be more liberal so that the public sector commercial banks make decisions in the face of changing business conditions. There is no doubt in it that the commercial banks bear the responsibility of energizing the social marketing, they are also supposed to bear the social costs. It is also right that the foreign banks have been found making the business environment more competitive. These emerging trends necessitate a close look on the pricing problem. The policy makers find it difficult to bring a change since the regulations of the RBI make things more critical. The expenses are not regulated by the RBI and the banking organizations are forced to increase the budgetary provisions. The sources of revenue are regulated which complicates the task of bank professionals. This makes it essential that the Reserve Bank of India, the Government of India and the banking organizations thing over this complicated issue with a new vision.
THE PLACE MIX
This component of the marketing mix is related to the offering of services. The two important decision making areas are making available the promised services to the ultimate users and selecting a suitable place for bank branches.
The selection of a suitable place for the establishment of a branch is significant with the viewpoint of making the place accessible and in addition, the safety and security provisions are also found important. The banking organizations are not free to open a branch since the Reserve Bank of India regulates the subject of branch expansion but so far as the management of branch is concerned, the branch managers have option to select a place which is convenient to both the parties, such as the users and the bankers. In the Indian perspective, the protection to the bank’s assets and safety to the users and bankers need due weightage. The vulnerable area or regions need adequate provisions to make the branch safe. The management of office is also found significant with the viewpoint of making the services attractive. The furnishing, civic amenities and parking facilities can’t be overlooked.
Another important decision making area is related to the offering of services. This draws our attention on the behavioural profile of bankers. The bankers in general and the front-line-staff in particular bear the responsibility of making available the services-promised to the ultimate users without any distortion often a gap is found generated by front-line-staff that makes an invasion on the image of bank. The bank professionals or a branch manager is required to be sure that whatever the promise have been made regarding the quality of services are not distorted. The RBI and the different public sector commercial banks are required to manage the distribution process intelligently and professionally. Thus, the place mix is found to be an important decision making area which requires due attention, both at macro and micro levels. If the banking organizations sell the promises it is essential that the end users get the same without any distortion.
THE PEOPLE
Sophisticated technologies, no doubt, inject life and strength to our efficiency but the instrumentality of sophisticated technologies start turning sour if the human resources are not managed in a right fashion. Generation of efficiency is substantially influenced by the quality of human resources. It is against this background that a majority of the management experts make a strong advocacy in favour of developing quality people and late, the people management has been include dint he marketing mix of organizations is general and the service generating organizations in particular.
Not only the public sector commercial banks but almost all the public sector organization and albeit other government departments, of late, have been facing the problem of quality people resulting into inefficiency, deceleration in the rate of overall productivity and profitability or so. The front-line staff are rough and indecent, the branch mangers are helpless and even the bankers have been found involved in the unfair practices. The public sector commercial banks need to assign on overriding priority to the development of quality people majority of the management of the experts have realized the significance of quality people in the development of an organization and the boardrooms are also found changing their attitudes. The first task before the banking organisatoins at the apex level is to overhaul the recruitment processes. While fixing criteria for selection, they need to assign due weightge to the ethical values. The education and training facilities are required to be innovated. The process of identification and inculcation need to be managed carefully.
The foreign banks and the private sector commercial banks reward for efficiency and at the same time also demotivate the inefficient bankers. This helps them in improving the efficiency of even the inefficient people. The development of human resources makes the ways for the formation of human capital. Incentives, of course, inject efficiency and the organizations offering more incentives succeed in motivating the people.
- Having better and cost-effective control over operations.
- Enriching the job content of employees at all level (by reducing the drudgery of mundane operations and increasing the analytical content of their work).
- Improving the quality of decision-making, a must in the fast changing environment.
Thus, the key focus areas in which information technology can be employed are:
- Automated processing of back-office operations like processing of forms, policy customization and product selection, pricing and preparation of quotations, etc.
- Computer assisted telephone and intelligent voice processing for customer call handling, new business marketing or handling after office hours enquirer.
- Image processing for documents storage and retrieval, folder management (or all documents related to a customer), and work flow management for the movement of documents with the bank.
- Artificial intelligence and expert systems for complex decision-making like the appraisal of the creditworthiness of clients, designing of innovative instruments and strategy formulation.
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) for the systematic use of information which would facilitate the cross-selling of products.
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for company-wise communication and inter-connection of systems for the benefit of both the bank’s MIS and the customer.
- Office Management Systems for accounting and administrative support.
All the above systems should be “client-based systems” and not “line-of-business systems” since these would provide better marketing and service to clients, facilitate cross-selling and customerization of schemes and hence, a better packaging for the product. This would help Indian banks “thing customer”.
All these would, thus, help in the effective management of time. Recourse to mechanized systems like ledger posting machine, cash counting machine and cheque sorting machine would result in reduction in the number of tedious and routine jobs to be handled manually saving time for the people to focus on the customer.
STRATEGIES FOR EFFECTIVE BANK MARKETING IN INDIA
Introduction: Since the inception of globalization in India, banking sector has undergone various changes. Introduction of asset classification and prudential accounting norms, deregulation of interest rate and opening up of the financial sector made Indian banking sector competitive. Encouragement to foreign banks and private sector banks increased competition for all operators in banking sector. The protective regime by the authority is over. Indian banks are exposed to global competition. Even competition within the country has increased manifold. The almost monopoly position enjoyed by the public sector banks of India is no more existence. Under this development Indian banks needs to reinvent the marketing strategy for growth.
The spread of the bank in Indian rural and semi urban areas are highly different from state to state and region to region. Many states have fewer networks of bank branches in the rural areas. Under such scenario different marketing approach for different areas is required. If the bank follows the same marketing strategy for all areas the success would be difficult.
Marketing approach for urban area: The urban areas of India are developed taking into account all parameters of development. The level of income of the people, the literacy rate and level of education as well as awareness of the people about rights of the customer are higher than that of the rural and even semi urban areas. Thus here for effective bank marketing different approach is necessary than that of rural areas.
The marketing strategy should be based on customer service and the use of modern technology in banking. Under competitive environment for the success of the business, better customers and retaining existing customers is possible only with customer service. Use of modern technology in urban areas will also go long way for marketing of banking services. Technology based service like credit card, debit card, ATM, anywhere banking, internet banking, and mobile banking are necessary for urban areas. This is because it enables customers to perform banking transactions at their convenience. Business hours of a bank are also an important factor for urban banking. India many private sector banks, especially co-operative banks and now even some of the public sector banks have also started this practice and they find it successful. To attract business and wholesale customers, banks need to adopt technology based product and service which is suitable to such class of customer. For instance RTGS, collection of out station cheques, issuing the cheques at par at any branch in the country, cash management facility, DD butiques etc. are necessary.
Another strategy for effective marketing is bank need to change the focus from the traditional banking to universal banking. In urban areas the extend and variety of economic activities demands that one institution should meet all financial need of a customer. Under such an expectation of people universal banking would prove successful approach for bank marketing. The term ‘universal banking’ in general refers to the combination of commercial banking and investment banking, i.e., issuing, underwriting, investing and trading in securities.
A universal bank is a supermarket for financial products. Under one roof, corporate can get loans and avail of other handy services, while individuals can bank and borrow.
For increasing customer base and retention of the existing cliental universal banking approach is effective strategy. Universal banking offers number of benefits to customers as well s the banks. For instance, economies of scale arise in multi-product firms because costs of offering various activities by different units are greater than the costs when they are offered together.
Universal banking with focus on retail customers made the ICICI banks to acquire first position in Indian banking sector. Universal banking approach is beneficial to bank also. For banks economies of scale relate to cost-savings through sharing of overheads and improving technology by jointly providing generically similar groups of services. Since universal banking basically provides financial services the inputs like manpower, infrastructure is more or less same. Necessary changes in the inputs can be made easily. For instance training can be given to staff for providing different financial services to customers. Moreover the most important benefit for the bank is that it is useful to increase the fee based income of the bank. Financial sector passing from lower interest rate regime at present and added to this the process of disintermediation is affecting the main and the traditional source of income for the banks i.e. interest income. All banks are striving hard to increase their fee based income to improve their bottom line. Universal banking can help the banks here positively.
Marketing approach for rural areas: Prior to nationalization of banks in 1969, the rural areas were virtually without banking facility. At that time unorganized sector was dominating in the rural finance. After nationalization of banks in 1969 branches of the banks were started gradually in the rural areas also. To day more than 50 percent branches of the banks are found in the rural areas. However, the distribution of banks in the rural areas is highly uneven. Here banks have to face competition with the unorganized sector. Moreover the rural banking is highly regularized activity by the Government in India. Lending as well as interest rate is regularized. Thus under such environment different marketing approach is required. For effective rural marketing product development, promotion and communication is important. All these parameters banks have to balance with socio-economic factors prevailing in the rural areas. Bank need to innovate product that could attract the depositors. Various loan schemes that are suitable for them for getting funds at right time and also they find convenient to repay. For instance traditional saving bank account may be given fixed deposit concept that once a particular limit of balance is reached the funds from saving account is automatically coveted into fixed deposit attracting higher interest rate.
Banks need t develop some scheme which would attract them to bank with. For loans and advances products which are suitable to farmers, small traders, small scale agro based rural industries are already in existence. Banks need to see the how value addition can be mad to these existing scheme. Banks also needs to tie up with Non Government Organisations and various Self Help Group for different types of loans, micro financing etc. This will help the bank for building good image and reputation in the rural areas over and above the business. Another potential area which can be explored by the banks in the rural area is retail banking. With the steady increase in the income of the rural people there is ample scope for retail loan products like housing loans and loan for consumer durables.
Marketing through customer services in rural areas is different from that of urban areas. Here personalized banking is the success mantra for banks. Because of high level of illiteracy people prefer to undertake banking transaction themselves. They hesitate to depend upon technology based service. For effective marketing in rural areas bank should have staff with right soft skill like concern for customers’ problem, positive attitude, good communication and negotiation skill. At every level of dealing with the customer bank need to educate them for banking activates and process. To attract the customers from the unorganized sector most important factor is to provide. The borrower the required finance of right amount at right time.
CONCLUSION
Banking sector has undergone various changes after the new economics policy based on privatization, globalization and liberalization adopted by Government of India. Introduction of asset classification and prudential accounting norms, deregulation of interest rate and opening up of the financial sector made Indian Banking sector competitive. Encouragement to foreign banks and private sector banks increased competition for all operators in banking sector. Banks in India prior to adoption of new economic policy was protected by Government and was having assured market due to almost state monopoly in banking sector. However, under the new environment, Indian banks needs to reinvent the marketing strategy for growth. In India geographical development is not even throughout the country, there are full-fledged urban areas covering the metropolitan cities and other big cities. On the other hand there are underdeveloped rural areas too. For effective bank marketing different approach for different areas is required. In urban areas customer services is of paramount importances as the level of literacy and therefore awareness of the people is more. Also technology based marketing would have higher degree of success due to typical urban life style of the people. Universal banking providing all financial service under one roof will have more success in urban areas. In the rural areas for bank marketing personalized banking will go in long way. Also banks need to offer innovative tailor made deposits and advances products to suit individual customers. Delivery of advances of right amount of right amount and at right time is essential in rural marketing.
TECHNOLOGY IN BANKING
Technology is proving to be a vital tool in enhancing banking activities around the globe. The advent of ATMs, and Internet Banking are key pointers to this. The role of an information system can in no way be underestimated. The expanding role of information systems have aided banks achieving Anytime, Anywhere and Anyhow banking. The improvement in telecommunication infrastructure is redefining the was banking is being conducted.
Information Technology made its presence felt in banks in India a few decades ago. However, it is still being used as a support systems. Most of the software packages used in bank work on stand-alone systems and are not integrated.
Banks in India need to have an integrated systems that takes care of all the front-office and back-office operations. However, Indian banks should not be content with the integration of their activities. Banks in advanced countries are planning to have global electronic banking. Electronic banking or e-Banking is a generic name for a range of technologies that allow the electronic exchange of information related to banking transactions.
As Electronic Networks become more robust and widespread, they are beginning to attract the attention of retail banks – like ATMs and phone banking. However they tend to be viewed merely as one more cheap distribution channel. Accordingly banks are replicating the branch banking experience online, even to the extent of creating 3D virtual branches for their customers to navigate through. Such an approach is characteristic of early attempts to use new technology platform.
Indian Banks Cash in on Delivery Channels
From the staid over-the-counter delivery mode to ATMs, tele banking, Net banking, and now mobile banking the number of delivery channel deployed by banks has increased by leaps and bounds. Srikanth R.P. & Chitra Padmanabhan look at the evolution and impact of various delivery channels in the Indian banking scenario and forecast which delivery channel could be the next killer app for banking players.
While today each and every bank touts ‘The customer is King’ mantra, it was a quite a different story not so long ago. Customers patronizing PSU banks were greeted with the typical ‘babu’ culture, where getting even a cheque encashed used to take ages. Customers had to adjust their schedule to the bank and very rarely was it the other way around. A person in a city like Bombay usually had to wait for a weekend to deposit a cheque, because by the time he reached home, the bank would have closed. Today, while the timings of banks have not changed drastically – banks have become more customer – friendly. Now power has shifted into the hand of the customer.
ATM (AUTOMATED TELLER MACHINES)
Traditionally, banking players relied extensively on their reach to effectively put emerging banks out of competition. This forced new banks develop strategies, that could help them reach out to end-customers cost effectively. The solution came in the from of a delivery channel known as Automated Teller Machines or ATMs. And when new private banks started installing ATMs across the length and breadth of the country, customers started flocking in droves. A case in point is ICICI Bank. During the liberalization of the banking sector, ICICI Bank which did not have a huge national network, realized that it could use IT to enhance its value-added offerings.
Says O.P. Srivastava, head of the retail channel infrastructure group at ICICI Bank, “When the banking sector was liberalized we knew that to get a lead over the well entrenched PSU banks, we had to take the help of delivery channels like ATMs. This was the only way to counter the reach of national players. “ICICI Bank is the most aggressive deployer of ATMs and has seen its base surge from 125 ATMs in January 2000 to 1,200 ATMs today. Such has been the impact of ATMs that ICICI Bank’s customer base has grown from two million to five million in the last two years. Srivastava attributes this increase to the increase in ATM outlets.
HDFC Bank, is the other big player from the banking industry which has aggressively used ATMs to its advantage. Says Mudit Saxena, vice-president for retail marketing and head of Net Banking at HDFC Bank, “The average per-day transaction at an HDFC Bank ATM is 350-400, with some ATMs recoding as many as 700 transactions per day”. Other tech savvy banks like UTI Bank and ABN Amro Bank have also become extremely aggressive in installing ATMs.
In the case of UTI Bank, the ATMs have added a fillip to the bank’s customer base. Says V K Ramani, president for IT at UTI Bank, “Form the first year of ATM installation, we have seen a surge in our customer base. Currently, we have 647 ATMs servicing a base of 1.3 million customers. Over 90 percent of cash withdrawals are done through ATMs. The number of ATM transactions have also increased from one million in September 2001 to over 2.5 million in September 2002.” With growth figures like this, its no wonder that every branch manager wants an ATM installed in his area of operations.
Alok Shende, Industry manager for IT practice at Frost & Sullivan, summarieses the evolution of the Indian banking industry perfectly when he says, “Banks followed two broad approaches when adopting technology. The first approach was evolutionary. Banking players who had large brick and mortar legacy particularly the public sector banks, kept the banking channels intact and automated the bottleneck points. This approach was adopted by around 80 percent of the industry. However, some banks adopted a revolutionary approach and changed the banking scenario altogether. State Bank of India is a good example of the evolutionary approach, whereas HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank, are good examples of the revolutionary approach. “Some banks have gone a step ahead and share their ATMs with other banks. For instance, ABN Amro Bank has a private ATM sharing agreement with UTI Bank.
Banks are also developing new strategies to leverage their ATM outlets. For instance, rather than set up a branch in every suburb, ICICI Bank has hit upon a ratio of 8 ATMs to one branch office, thus effectively reaching out to a large customer base, at a substantially lower cost.
ABN Amro launched Royalties, India’s first banking rewards programme. In the programme, the customer gets rewarded every time he uses any of the bank’s electronic access channels. If the customer bites the bait, it not only reduces the work load, but also translates into huge cost savings.
As PSU banks gear up to win back their customers through the aggressive deployment of ATMs, the already vibrant ATM market has got a further boost. In India, ATM manufacturers like NCR and HMA Diebold are extremely bullish, as India is the fastest growing market for ATMs currently. India has close to 7,500 ATMs and analysts predict the market to grow at a rate of 60-70 percent year-on-year. Looking at the boom in ATMs NCR has decided to invest $6 million to set up its ATM manufacturing plant in India.
Says Lars Nyberg, chairman and chief executive officer of NCR, “India is undoubtedly the hottest market for ATMs today. Our decision to manufacturer in India is to accelerate supply to the local market. Initially, the manufacturing facility in Bangalore will have a capacity of produce 8,000-10,000 ATMs per year. “The potential of the Indian market has prompted NCR to design at ATM specifically for the Indian market.
Total cost advantage
While ATMs do help banks to attract customers, there is also one more critical aspect to consider – the immense cost savings from which a bank can benefit due to a transaction taking place over an ATM vis-à-vis a branch. Typically, it costs a bank close to Rs. 50 per transaction if conducted in a branch. The same if done an ATM costs about Rs. 15. A look at the volume of ATM transactions conducted reflects the level of success of this delivery channel.
Internet Banking
The other important delivery channel, from a bank’s perspective & Internet banking. The adoption of Internet banking by the bank’s customers is important since the costs per transaction are even lower than those of an ATM. A net-based transaction costs the bank only around Rs. 4. Thus, banks are trying to get customers to switch over to this mode of banking registered users for Internet banking in India at over two million currently.
It represent a significant opportunity for banks. In addition, as a delivery channel, Internet banking does not require physical infrastructure, thus saving on prohibitive real estate costs.
Private banks like ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, UTI Bank and ABN Amro Bank have seen a steady surge in the number of users registered for Internet banking does not require physical infrastructure, thus saving on prohibitive real estate costs.
Most banks today have facilities to enable internet banking customers to pay insurance premiums and utility bills over the Net. Though Internet banking as a concept has not caught the fancy of a majority of customers as yet-even the small percentage that does use it, makes a difference to the overall cost. Almost all leading banks in India are hoping that just as ATMs saw a period of inaction before they were accepted by Indian masses, Internet banking too would be adopted once customers are comfortable with the technology. For instance, in 1998 India had just 500 ATMs today it has close to 7,500.
Roadblocks
While Internet banking is a potential and powerful delivery channel, it has failed to make a significant impact due to a variety of reasons. RBI in its report, ‘Trend and progress of Banking in India, 2001-02, says Internet banking has failed to take off due to a combination of psychological, technological and socio-economic factors. Further, the report states that additional hurdles relating to legal and infrastructural problems have also affected growth.
Although the government has made considerable progress in initiating a trust environment, with some Public Certification Authorities (PCA) already licensed to operate, the adoption of trust technology is still a daunting factor for many users. What needs to be developed is a simple way of integrating trust into online banking services.
Says Shende, “The compelling restraint for the user is the fear of security breaches. As long as the perceived notion that the Internet is not a safe place to conduct financial transactions prevails, large scale adoption will be challenging.” In addition, the low penetration of PCs and access to the Internet are crucial issues which act as roadblocks in the adoption of Internet banking.
MOBILE BANKING
What’s M-Banking?
M-Banking allows a customer to request for account balance, cheque books, cheque status, demand drafts, and banker’s cheques as well as stop payments, make fixed deposits inquiry and transfer bills online. HDFC customers, for instance, can pay their Max Touch and BPL Mobile both provide cellular services – Bombay State Electricity Supply, and Maharashtra State Electricity Board bills. Says Shyamlal Saxena, 33, Vice President (Liabilities Product Management), HDFC: “WE are, in a sense, content providers of banking information.”
Is it Better?
M-banking is no different from Net Banking, in fact it has many limitation. You still cannot transfer fund from one bank to another and, given the high air-time charges, it works out much more expensive than Net Banking. And for the mobile phone to access a site, the contents must be in Wireless Markup Language.
Once the mobile users’ population grows, access rates will fall, allowing customers to use more air-time. By then, the Reserve Bank of India would also have put its own gateway in place to do online what it does today on paper.
M-banking uses two kinds of communication technologies. One is WAP (Wireless application Protocal) and the other is SMS (Short Messaging Services). WAP is more user-friendly, as it allows download of graphic information. SMS, in contrast, allows text-only access. But as the time taken to download text is much les compared to graphics, SMS is cheaper to use.
Future Delivery Channels
Among all the delivery channels used by banks today, ATMs remain the most successful, followed by telephone banking and Internet banking. But the biggest potential could lie in mobile banking. With cellphone tariffs falling and increased bandwidth, the potential for banking player to tap this channel is enormous. Says Raman, “The future delivery channel will have various mobile portals using technologies such as GRPS. The customer would prefer to do banking transactions not only anytime, anywhere, but also through any device. With the current rate of evolution in the wireless industry, the mobile channel is poised to become the de-facto banking channel within the next three years.”
One more important factor to consider in the evolution of delivery channels is the requirement of a multi-channel architecture which should support all future delivery channels, while also seamlessly integrating with existing delivery channels. This is the reason why a majority of banks still have not launched Internet banking as a feature, since most do not have backend integration. Effectively, this means that if a person holding an account with the bank wants to apply for a loan, he would have to enter the same details already disclosed earlier to the bank. This is where players like HDFC Bank, Citibank or ICICI Bank hold an edge, as they have an end-to-end integrated system already in place. This gives them the ability to cross-sell their products, based on the customer profile they have with them.
one more delivery channel which will increase in the future is the deployment of call centres. For instance, looking at the cost effectiveness of call centers, ICICI Bank has commissioned the country’s biggest call centre in the banking sector (1,100 seats) in Hyderabad. This is to be followed by a 600-seat call centre in Mumbai)
As a delivery channel gains ground, it can be used to sell products of other vendors too. For example, the SBI ATM at CST railway station in Mumbai dispenses season tickets too. Analysts believe that as banks discover the marketing power of ATMs, one would see a trend where ATMs would be used to deliver products of other vendors as well. ICICI Bank has gone one step further by allowing devotees of Tirupati to offer payments to the temple at Tirupati temple through their ATM.
This could be the future of ATMs, where more non-cash transactions will be done. Some banks are even toying with the idea of selling movie tickets through ATMs. Going forward, as the volume of non-cash transactions increase, one can see a trend where banks maintain kiosks instead of ATMs, as there might not be a need for all the features of an ATM.
Says Chopra of ABN Amro, “The next five years will see a marked shift, wherein customers will show a preference for non- branch delivery channels. Also, the large number of customer calls will also necessitate use the of toll free numbers.”
Irrespective of the delivery channel, one thing is clear-it’s boom time for customers, as banks try a variety of options to lure them
Who knows, the next time you go to deposit your cheque, you just might fill in ‘Virtual’ in the space reserved for ‘Branch’.
BANK MARKETING IN THE INDIAN PERSPECTIVE
The level of income, expectations, the rate of literacy, the geographic and demographic considerations, the rural or urban orientation, the changes in economic systems the frequent use of, technologies are some of the key factors governing the development plan of an organization. To be more specific in a welfare country like ours, the public sector commercial banks are supposed to play decisive role in fueling the processes of socio-economic emancipation. This makes it clear that the banking organization need a new vision, a new approach and an innovative strategy. They are supposed to bring about greater mobility in the financial resources to cater to the changing socio-economic requirements. Willingly or unwillingly, they have also to bear the social costs by advancing credit facilities to the weaker sections and the vulnerable regions. The foreign banks and a few of the private sector commercial banks have been found making sincere efforts to improve the quality of their services. The customers in general appreciate the functional style and service mix of foreign banks. This makes a strong advocacy favor of practicing marketing principles in the public sector commercial banks.
The nationalization of the Reserve Bank of India is a landmark in the development of Indian banking system which in a true sense paved avenues for qualitative-cum quantitative improvements. Acquisition of extensive powers of supervision and control by the Reserve Bank of India under the Banking Regulations 1949 opened new vistas for the expansion of banking facilities. The structure of public sector bank was further strengthened in 1959. To curb concentration of economic power and promote a judicious use of the financial resources for the economic development activities, the banking system was regulated and supervised by the RBI subsequently in 1969 the Government acquired a direct control over a substantial segment of the banking system signifying its commitment to reshape the banking system so as to meet progressively and serve better the needs of the development of economy in conformity with the changing national policy and objective. The fruitfu11 results of nationalization of 14 commercial banks in 1969 encouraged. government to nationalize more commercial banks in 1980. These developments necessitated a fundamental change in the functional responsibilities of the public sector commercial banks. Here it is pertinent to mention that nationalization was with the motto of improving the quality of services but the public sector commercial banks started disappointing the masses. Of late, the quality of services is so poor that customers in general are found dissatisfied. This makes it essential that the Reserve Bank of India and the policy makers of the public sector commercial banks think in favor of conceptualizing modern marketing principles which would bring a radical change in the process of quality up-gradation.
The first task before the public sector commercial banks is to formulate the marketing mix which suits the national socio-economic requirements. They need to synchronize the core and peripheral services in such a way that product attractiveness is increased substantially. To be more specific the peripheral services need frequent innovation, since this would be helpful in excelling competition. The personal selling and public relations activities need an intensive care. It is pertinent to mention that the leading foreign banks have been found promoting telemarketing and the public sector commercial banks need to make it possible. Since we have world class communication technologies, the task is easier. The word-of-mouth promotion also needs due care and for that we need to improve the quality of services vis-à-vis the cooperation of opinion leaders. The Reserve Bank of India and the Indian Banking Association need an attitudinal change. The boardrooms also need to change their attitudes. The gap between the services-promised and services-offered is required to be bridged over. This requires professional excellence. The professionals need to make possible a fair synchronisation of performance-orientation and employee orientation. This is not possible unless the banking regulations are made liberal. The quality of people/employees serving the banking organizations needs an overriding priority. The bankers need to know about the behavioural management. The front-line-staff need empathy in their behaviour. This requires intensive training facilities. The domination of trade unions is required to be minimised. The contractual job system needs due attention. The bank professionals need to assign due weightage to their physical properties. They are supposed to look smart, active and attractive. Thus we need multi-dimensional changes which make a strong advocacy in favour of implementing the innovative marketing principles.
In view of the above, it is right to mention that in the face of new perception of quality developed by the foreign and private sector commercial banks, the public sector commercial banks have no option but to improve the quality of services. The marketing principles bear the efficacy of initiating qualitative improvements. It is against this background that we go through the problem of bank marketing. Of late the foreign banks have been found promoting the use of sophisticated information technologies. This makes it essential that we realize gravity of the situation and make possible a rational use of technologies which is not to aggravate the problem of retrenchment. The marketing principles would be helpful in making an assault on the multi-dimensional problems. Of course, we find good auguries because the policy makers have been found exploring ways for implementing the marketing principles but till now, the efforts are at the very nascent stage. It is high time that the public sector commercial banks conceptualize innovative marketing for bringing the banking system on the rail.
The first thing is that the future of bank marketing is gonna be fabulous. If you are thinking to go for field than you must…You can study the charts how it rose since last 5 years and you will he impressed. In past bank were not in competition with each other in India but now they are and that’s where bank marketing is coming up…eg. In Ahmadabad ICICI rose by 70% in terms of advancing loans to local public…Sales guys are doing very well.,This is going to rise until 80% of Indians are not having credit cards.. Compare the banking to developed countries and you will find bank marketing in India to be great.
The bank of the future has to be essentially a marketing organization that also sells banking products. New distribution channels are being used; more & more banks are outsourcing services like disbursement and servicing of consumer loans, Credit card business. Direct Selling Agents (DSAs) of various Banks go out and sell their products. They make house calls to get the application form filled in properly and also take your passport-sized photo. Home banking has already become common, where you ~an order a draft or cash over phone/internet and have it delivered horn. ICICI bank was the first among the new private banks to launch its net banking service, called Infinity. It allows the user to access account information over a secure line, request cheque books and stop payment, and even transfer funds between ICICI Bank accounts. Citibank has been offering net banking to its Suvidha program to customers.
Products like debit cards, flexi deposits, ATM cards, personal loans including consumer loans, housing loans and vehicle loans have been introduced by a number of banks.
Corporates are also deriving benefit from the increased variety of products and competition among the banks. Certificates of deposit, Commercial papers, non-convertible Debentures (NCDs) that can be traded in the secondary market are gaining popularity. Recently, market has also seen major developments in treasury advisory services. With the introduction of Rupee floating rates for deposits as well as advances, products like interest rate swaps and forward rate agreements for foreign exchange, risk management products like forward contract, option contract, currency swap are offered by almost every authorised dealer bank in the market. The list is growing.
Public Sector Banks like SBI have also started focusing on this area. SBI plans to open 100 new branches called Personal Banking Branches (PBB) this year. The PBBs will also market SBI’s entire spectrum of loan products: housing loans, car loans, personal loans, consumer durable loans, education loans, loans against share, financing against gold.
The bank of the future has to be essentially a marketing organisation that also sells banking products. New distribution channels are being used; more & more banks are outsourcing services. ICICI bank was the first among the new private banks to launch its net banking service, called Infinity.
Products like debit cards, flexi deposits, ATM cards, personal loans including consumer loans, housing loans and vehicle loans have been introduced by a number of banks.
Public Sector Banks like SBI have also started focusing on this area. SBI plans to open 100 new branches called Personal Banking Branches (PBB) this year. The PBBs will also market SBI’s entire spectrum of loan products: housing loans, car loans, personal loans,
Always Yours—– As Usual —— Saurabh Singh



















Impressions of Visitor & Few Replies